CONFIANZA
SEGURIDAD
FLEXIBILIDAD
DEFINITIONS
What Is a Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed database that is shared among the nodes of a computer network. As a database, a blockchain stores information electronically in digital format. Blockchains are best known for their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, such as Bitcoin, for maintaining a secure and decentralized record of transactions. The innovation with a blockchain is that it guarantees the fidelity and security of a record of data and generates trust without the need for a trusted third party.
One key difference between a typical database and a blockchain is how the data is structured. A blockchain collects information together in groups, known as blocks, that hold sets of information. Blocks have certain storage capacities and, when filled, are closed and linked to the previously filled block, forming a chain of data known as the blockchain. All new information that follows that freshly added block is compiled into a newly formed block that will then also be added to the chain once filled.
TOKEN
The term crypto token refers to a special virtual currency token or how cryptocurrencies are denominated. These tokens represent fungible and tradable assets or utilities that reside on their own blockchains. Crypto tokens are often used to fundraise for crowd sales, but they can also serve as a substitute for other things. These tokens are usually created, distributed, sold, and circulated through the standard initial coin offering (ICO) process, which involves a crowdfunding exercise to fund project development.
Tokens can be used for investment purposes, to store value, or to make purchases
WALLETS
Tokens are stored on cryptographic wallets ("Wallets"). A private key (for example, a passphrase) is usually necessary to access, control and/or dispose of tokens that are stored in your Wallet. Losing access to the private key(s) associated with your Wallet may result in the permanent loss of your ability to access and dispose of your tokens.
Crypto tokens are cryptocurrency tokens. Cryptocurrencies or virtual currencies are denominated into these tokens, which reside on their own blockchains. Blockchains are special databases that store information in blocks that are then chained or linked together. This means that crypto tokens, which are also called crypto assets, represent a certain unit of value.
Here's how it all works. Crypto refers to the various encryption algorithms and cryptographic techniques that safeguard these entries, such as elliptical curve encryption, public-private key pairs, and hashing functions.Cryptocurrencies, on the other hand, are systems that allow for secure payments online which are denominated in virtual tokens. These tokens are represented by ledger entries internal to the system.
LEDGER
A public ledger is a record-keeping system. The ledger maintains participants' identities anonymously, their respective cryptocurrency balances, and a record of all the genuine transactions executed between network participants.
Hardware wallets are a form of offline storage. A hardware wallet is a wallet that stores the user's private keys (a critical piece of information used to authorize outgoing transactions on the blockchain network) in a secure hardware device.
Ledger's hardware wallets are device-based, which means they use storage mechanisms—USB drives—to store private keys, thereby making it difficult for hackers to access the key from an online location.
PROTOCOLS
Tokens are recorded on distributed ledgers (typically shared across networks of users) which are governed by, subject to, and distinguished on the basis of certain set of rules known as protocols.
Malfunction, breakdown and/or abandonment of protocols
Any malfunction, breakdown, and/or abandonment of the protocols (and of any consensus mechanism, where applicable) on which the tokens are based could severely affect the price of the tokens as well as your ability to dispose of the tokens (particularly where the protocol relies on substantial participation and wide networks to operate properly).

Certification, inspection and auditing solutions focused on business optimization.
CONFIDENCE
SECURITY
FLEXIBILITY
How Does a Blockchain Work?
The goal of blockchain is to allow digital information to be recorded and distributed, but not edited. In this way, a blockchain is the foundation for immutable ledgers, or records of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed. This is why blockchains are also known as a distributed ledger technology (DLT).
Is Blockchain Secure?
Blockchain technology achieves decentralized security and trust in several ways. To begin with, new blocks are always stored linearly and chronologically. That is, they are always added to the “end” of the blockchain. After a block has been added to the end of the blockchain, it is extremely difficult to go back and alter the contents of the block unless a majority of the network has reached a consensus to do so. That’s because each block contains its own hash, along with the hash of the block before it, as well as the previously mentioned time stamp. Hash codes are created by a mathematical function that turns digital information into a string of numbers and letters. If that information is edited in any way, then the hash code changes as well.
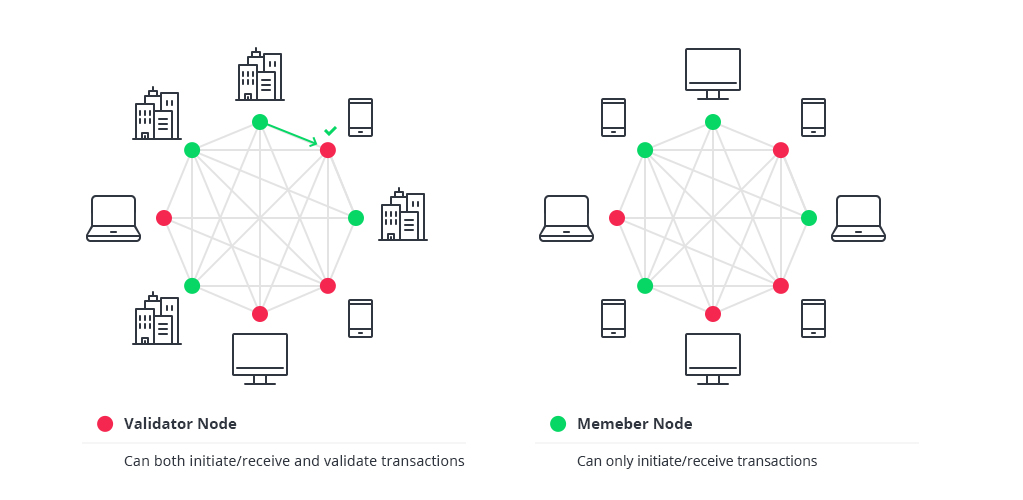
Types of Blockchain Architecture Explained
Nodes in Public vs. Private Blockchains

NOTA: ESTA WEB NO UTILIZA COOKIES NI NINGÚN MEDIO DE CONTROL VISITANTES.
INTERCER
Avda. del Conocimiento nº 34, Parque Tecnológico de Ciencias de la Salud , 18006 Armilla, Granada, Spain
Copyright INTERCER. All rights reserved.

